Wellbeing in Retirement
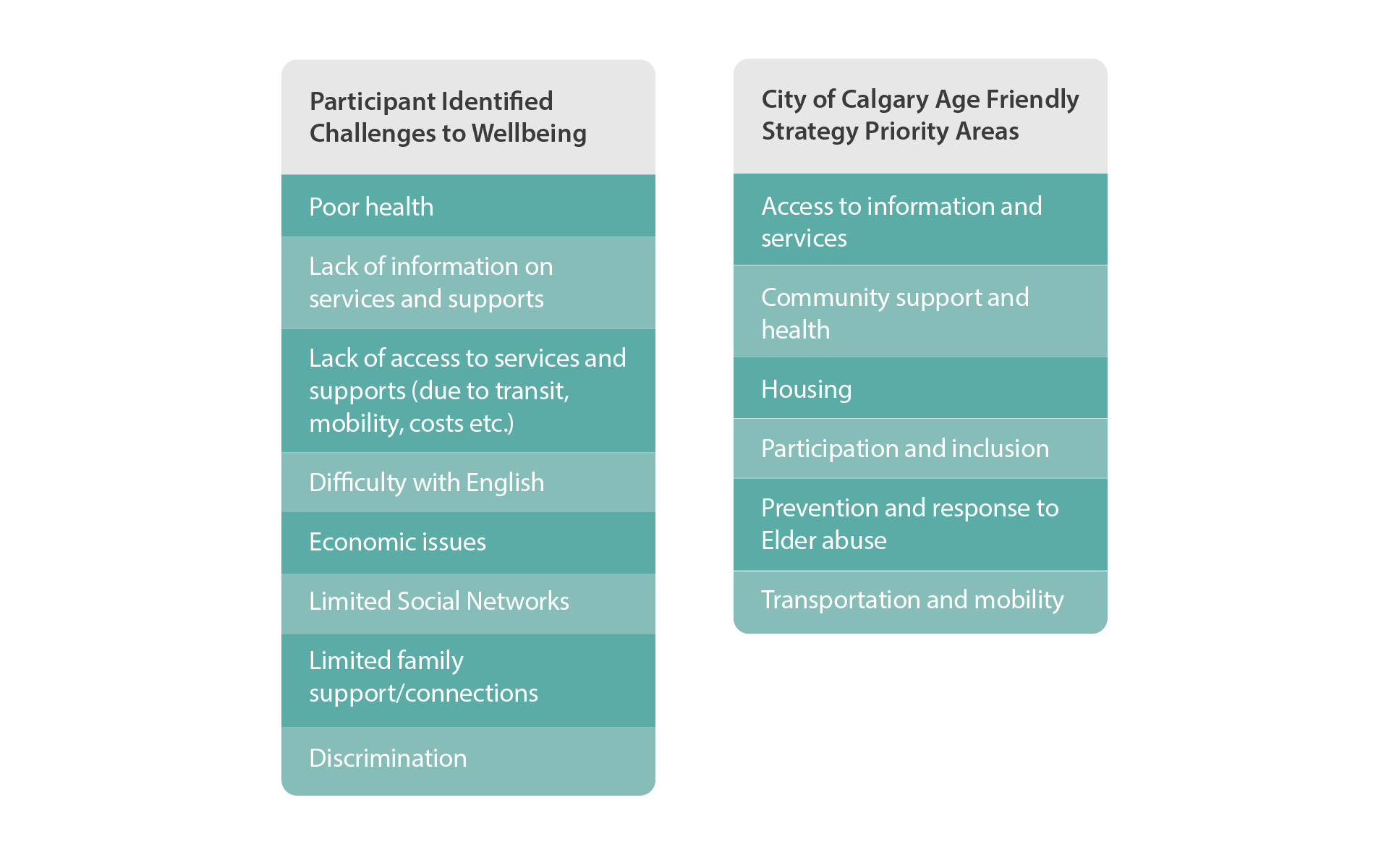
Wellbeing in retirement is shaped by physical and mental health, finances, family circumstances, and working circumstances but also moral notions of what activity and social participation should look like after leaving the traditional full-time work world (Kojola and Moen 2016).
The participant-identified factors of wellbeing in the figure below align with existing research on wellbeing and healthy aging. Further, the factors clearly align to the World Health Organization’s (WHO) eight identified areas for age-friendly cities: transportation, housing, social participation, respect and inclusion, civic participation and employment, communication and information, community supports and health services, and outdoor spaced and buildings (2007). Together the WHO’s factors of age-friendly cities intersect to create the social and structural conditions that enable the contributing factors of wellbeing.